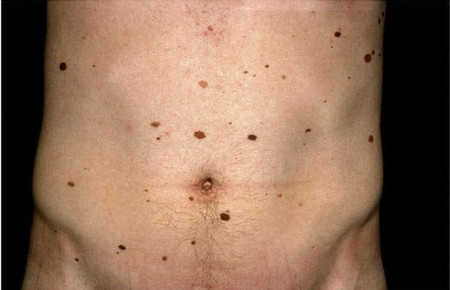
Brown spots in the form of moles on the body. Signs of a malignant mole
Are congenital or acquired skin defects. They occur everywhere: on the torso, fingers, face, etc. Moles are characterized by a variety of shapes, shades and sizes. Often they are called nevi. Such neoplasms are flat and convex, with a smooth or hairy surface.
They may be present at birth or occur throughout life. The presence of an excessive number of nevi indicates the negative impact of ultraviolet radiation or a hereditary tendency to form moles.
By themselves, nevi are safe for the body, but in the presence of some negative factors, they are able to become malignant or form in malignant neoplasms, subsequently leading to . Such nevi are called melanoma dangerous.
dangerous species
Oncologists identify 5 dangerous types of moles:
- looks like a spot with the same color over the entire surface, which can reach an almost black tint. Such moles do not react to the influence of UV rays, do not change color, number and parameters;
- - a rather dense neoplasm with a smooth, hairless coating. Such a mole is noticeably higher than the skin, does not exceed 2 cm in diameter, prefers to be located in the area of \u200b\u200bthe limbs, face and buttocks;
- A giant mole is considered the most dangerous formation, since in half of the cases it is reborn. Such a nevus is characterized by a heterogeneous loose surface and annually increases in size;
- Nevus Ota - is a large dark brown or blue-gray mole. Such education requires mandatory treatment;
- - is considered a precancerous formation with an uneven contour. Such a formation, upon detection, requires removal, since in most cases it undergoes malignancy.
An experienced doctor will be able to identify the danger of a nevus by its appearance.
The statistics are such that most patients get to the oncologist too late, when the process of malignancy has already been completed and the harmless nevus has been reclassified into a cancerous tumor. The reason for this pattern is carelessness in relation to moles and ignorance of the main symptoms of rebirth.
Reasons for the degeneration of a mole into a malignant one
Nevi are prone to rebirth in the presence of irritating factors. For such changes may result from excessive ultraviolet exposure Therefore, it is extremely important to avoid long-term exposure to the open sun, especially at 11-16 hours.
This statement is confirmed by the fact that in sunny states, where residents are irradiated with ultraviolet light all year round, it is diagnosed much more often than in the northern regions.
Prove the ultraviolet conditionality of malignancy and recent studies. With every sunburn in childhood, the risk of developing a malignant nevus in adulthood increases. No less dangerous are various injuries to moles, in the event of which it is recommended to consult a specialist.
Not the last role in the malignancy of nevi is played by the genetic factor. If a person at the genetic level lacks the ability to adapt to an aggressive environment, then it is referred to the risk group for malignancy of moles.
Main features
If you are a happy owner of moles, then make it a rule to examine them periodically in order to timely identify a possible rebirth. For ease of memorization, dermatologists have come up with such a diagnostic rule “chord”, according to which they reveal the symptoms of the degeneration of a mole into a malignant one:
- A is asymmetric. Benign nevi are distinguished by a symmetrical structure (except for congenital ones), and if a mole begins to acquire an asymmetrical shape, then this can serve as a signal of the beginning of rebirth;
- K - contours. If the edges of the nevus have become uneven, blurry, fuzzy, then such a fact should be a cause for alarm;
- Oh, shade. If the color of the mole has acquired any inclusions, dots or stripes, then this may indicate the development of rebirth;
- R - dimensions. A nevus can change its size only during the transitional age in adolescents, when puberty occurs. The remaining cases of sudden growth of a mole require the intervention of a specialist;
- D - dynamics of pathological changes. The sudden appearance of cracks, crusts, bleeding is evidence of malignancy of the mole.
In the photo you can compare how malignant and benign moles look
In addition to the above, characteristic features malignant mole are:
- Causeless peeling, changes in surface texture;
- Compaction of the nevus against the background of its rapid growth;
- It is dangerous if the mole starts to itch, there is a burning or tingling sensation;
- The sudden appearance of spots around the nevus, similar to an allergic rash.
If there is at least one sign, then this already requires a medical consultation and makes you think about the malignancy of the nevus. Therefore, you should not let any changes in the mole take its course, because the violation of the integrity of the surface layer of the nevus is dangerous by blood poisoning with a very unfavorable outcome.
Diagnostics
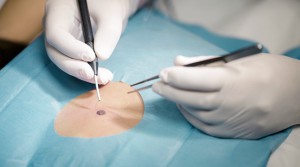
Only a doctor can independently determine the malignant nature of a mole after the procedure. Such a study does not cause pain and takes about 3 minutes per nevus.
The procedure is carried out with a dermatoscope - a specialized device that provides a diagnostic accuracy of about 95-97%.
What to do if the nevus turned out to be malignant
If the malignancy of the mole is confirmed by specialists and conducted diagnostic procedures, then the patient is usually referred for an operation involving the removal of a mole in an operative way.
Indications for removal
Not all moles need to be removed. There is a list of indications for the removal of nevi:
- If the mole has degenerated into a malignant formation (malignant);
- Large size of the nevus or its unaesthetic appearance;
- The presence of permanent injury of mechanical or chemical origin. If the mole is injured by clothing, causes discomfort and pain, bleeds, then it must be removed in order to prevent blood poisoning or malignancy.
Ways
Malignant moles are removed in various ways. There are 5 main techniques most often used to remove nevi.
- . A similar method involves the elimination of neoplasms by freezing with liquid nitrogen or a mixture of carbonic acid. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes a few minutes. The disadvantage of this technique is the inability to control the degree of nitrogen or acid exposure.
After cryotherapy, it is impossible to obtain biomaterial for histological examination. If the nevus was large, then after freezing, there is a possibility of scarring or scarring.
- laser treatment. It involves the removal of a mole by laser burning. The method has many advantages. One of them is the simultaneous sealing of blood vessels, which makes it possible to successfully apply such treatment to moles that are characterized by bleeding. There is also a minus - the impossibility of conducting histology.
- Radio wave therapy. A similar technique is acceptable for medium-sized nevi located on the surface of the skin. The procedure is carried out with a special apparatus (Surgitron, etc.), after which a quickly healing wound remains. Radiotherapy does not damage the tissues of the nevus, which allows subsequent histological examination. After the procedure, there are no scars, and the postoperative wound quickly disappears.
- Electrotreatment. Such therapy involves burning the nevus with low-frequency electricity. The procedure is very traumatic, there is a high probability of postoperative scarring, so this technique is rarely used. But electrocoagulation also has advantages - the possibility of histological examination.
- Surgical removal. A similar method is used to remove large moles or with deep germination of melanoma in the tissues on which it is located. Also, such an operation is applicable for flat nevi, tumors of a malignant nature and for malignancy of a mole. Cancer neoplasms are excised along with the surrounding skin.
If the patient wants to get rid of the nevus for aesthetic reasons, then it should be borne in mind that the mole can be permanently eliminated only if it does not exceed 5 mm. With a large size of the nevus, a scar will remain after removal.
Survival prognosis
The survival rate is usually determined by the thickness of the malignant mole. A similar criterion is called the Breslow depth. The depth of penetration of the oncological process, the Clark level, is also taken into account when predicting.
If the melanoma is less than 1 cm thick, then the prognosis is favorable. If the thickness of the nevus exceeds 1 cm, then the forecasts are less favorable.
Prevention
 Prevention of the degeneration of a benign mole into a malignant one has not been developed today, although there are several recommendations that can help prevent the process of malignancy:
Prevention of the degeneration of a benign mole into a malignant one has not been developed today, although there are several recommendations that can help prevent the process of malignancy:
- Be attentive to the condition of already existing moles, and if there are changes, contact an oncologist in a timely manner;
- Avoid long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation (solarium, beach), use UV protection;
- Avoid contact with chemicals.
Do not try to cut or tear off the mole yourself. This should be done only by a specialist and using the necessary equipment.
Video on how to recognize a malignant formation on the skin, diagnosis and treatment of a tumor:
A mole is a benign formation on the skin that appears due to the accumulation of melanocytes - pigment cells. The color of a mole depends on melanin, which accumulates in melanocytes. The more pigment, the darker the nevus will be. The color of the mole is affected by impaired blood flow in the capillaries. Because of this, they acquire a red tint. The color variation of neoplasms ranges from light brown to black. Health hazards are dark moles with fuzzy edges.
The color of moles in humans can be different, and some of them are characteristic of dangerous neoplasms.
Types of moles
There are many classifications of nevi. Classifications are often used according to the shape and type of tissue from which the neoplasms arose. Based on the histological variety, neoplasms are divided into melanoma-dangerous and melanoma-safe. The first type of nevi leads to oncology, the second is safe for humans. In the form of moles are:
- hair;
- convex;
- hanging;
- flat;
- warty;
- smooth.
If the mole is uneven in color or discolored, you should consult a dermatologist.
Non-vascular nevi according to histological classification are divided as follows:
- Dysplastic - brown neoplasms that do not have clear boundaries. Their appearance is genetically predisposed.
- Giant neoplasms - large spots, the color of which varies from gray to black. Often congenital, and increase with age.
- Sutton's nevi are surrounded by skin without pigment. They tend to spontaneously appear and disappear.
- Epidermal-dermal - occur in the limbs and genitals. Color from gray to black.
- Intradermal - characterized by a warty surface with hairs. Flesh-colored mole.
- Complex pigments are dark growths that rise slightly above the skin.
- Borderline - a cluster of small spots resembling freckles. Their number increases with age.
- Blue nevi are dark, usually blue, brown, or black. They have clear boundaries. Cellular blue growth can degenerate into melanoma.
Why are there different colors?
The reason for the "colorfulness" of the formations are pigment cells - melanocytes. They are evenly distributed throughout the skin. Melanocytes betray the color of our skin - from light pink in Europeans to dark brown in blacks. It all depends on the pigment that melanocytes produce. If their concentration is high in a certain area of the skin, then the pigment has a higher concentration than in neighboring areas of the skin. This leads to the appearance of moles. In fair-skinned people, the nevi are brown, in dark-skinned people - almost black. Red moles arise due to a violation of blood flow in the vessels: if the capillaries are damaged, then the growth will be small and pale, if the arteries or veins succumb to violations, then the pigment will be swollen and intensely colored.
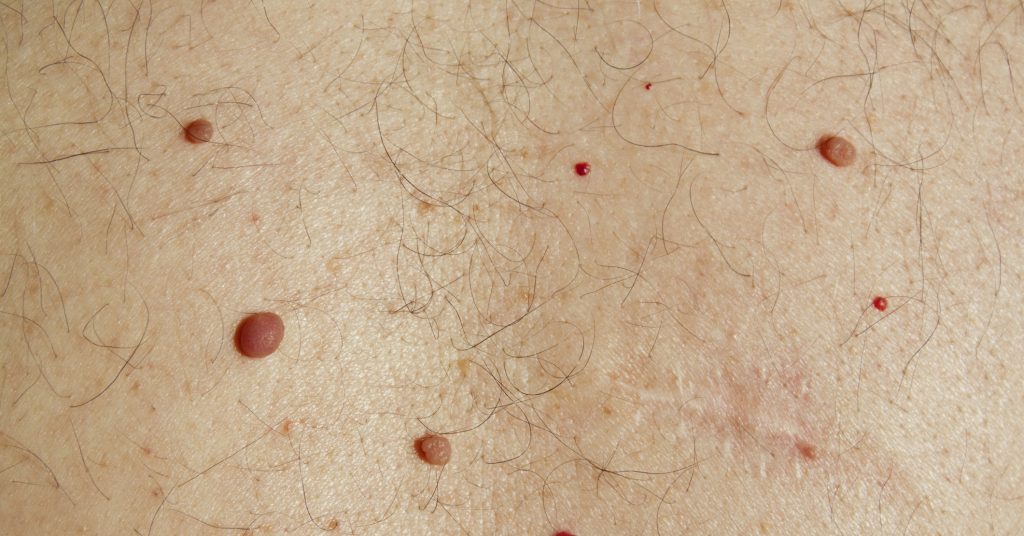 Brown (coffee) nevi are the most common on the human body and are not dangerous.
Brown (coffee) nevi are the most common on the human body and are not dangerous. What are the colors of moles on the body?
Brown
"Coffee spots" or brown nevi are the most common. They are small or medium in size, flat or convex in shape. Most of them are not dangerous to health. Neoplasms are found throughout the body, especially on the limbs. Actively occur in spring and summer under the influence of sun rays. This should be given special importance to people with fair skin, in whom this process goes faster. If such a mole on the face has increased in diameter by more than 2 cm, there is a possible risk of degeneration into an oncological disease.
Of red color
Angiomas or red nevi are of vascular origin. The exact origins are unknown. It is believed that the appearance of angiomas is affected by disturbances in the work of the large intestine and pancreas. Red moles appear in young children, but can also occur in adults. To prevent the occurrence of angiomas, you should regularly cleanse the intestines. By themselves, angiomas do not pose a health hazard, but if they increase in size, they can degenerate into skin cancer.
 Black moles in humans are not dangerous, but the “blackening” of light nevi is an alarm signal.
Black moles in humans are not dangerous, but the “blackening” of light nevi is an alarm signal. Every person has birthmarks on their body. different kind, textures, colors, shapes. These harmless formations arise in the epidermis from melanocytes and grow in clusters. The scientific name for a mole is a nevus. This medical term applies to all skin abnormalities. However, behind these so-called "flies" the most aggressive malignant tumor- melanoma.
Therefore, you should know what they are and be able to recognize the main differences between benign and malignant. Cancer transformations most often occur on the basis of pigmented skin tissues.
What moles are dangerous?
Cancer moles, like normal ones, are made up of melanocytes. But this is an aggressive form of the tumor, prone to rapid spread and damage to other organs. In this regard, it is recommended to be careful with such pigmented skin formations as:
Atypical nevi:
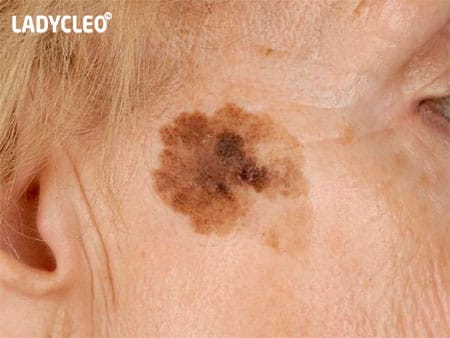
This appearance from the very beginning does not look like an ordinary birthmark, since its size is larger than a pencil eraser, the shape is fuzzy, and the color is uneven. Moreover, the potential danger is borne by congenital formations, and not acquired ones. Most of them are inherited and have a size of over 1 cm.
Hutchinson's melanotic freckles(lentigo):
Appear as a flat spot containing two or more shades of darkening. They are quite common after the age of 50 and are localized in particular on the face. Gradually become larger and darker, transforming into.
Skin neoplasms of unknown etiology:
Neoplasms that appear suddenly, develop very quickly, are outwardly aggressive and are not at all like the usual “fly”. In 60% of all cases of melanoma, this type of pigmentation functions.
Dangerous moles: signs
Color changes:
Potentially oncological is a mole that has begun a color change. For example, one-color pigmentation has acquired some other spots around or in the middle.
Altitude change:
An important feature is a change in the height of a previously flat spot, density (thickening).
Consistency changes:
For example, a mole softens, breaks into small pieces that break off easily, or resemble scratches that do not heal.
What moles are potentially dangerous?
There are certain categories of birthmarks that tend to transform into a malignant form. All of them relate to abnormal skin seals:
- Nodular pigmented nevi: usually brown or round and flat.
- Cutaneous pigmented nevi: have an elevated appearance, a pale color, sometimes a hairy surface.
- Connecting nevi combine elements of different formations.
- A halo nevus is a pigmented area of skin surrounded by a discolored white ring.
- Dysplastic nevus (other name Clark) is a specific neoplasm.
- Spitz nevus: looks like a tumor-like neoplasm on the skin. This spot is pink (but it is possible to combine different colors), domed, prone to bleeding. It may have a hole through which liquid seeps through.
- A blue nevus has one of the shades of blue, shows well-defined borders, any size (but more often does not exceed 1 cm), looks like a seal under the skin.
The main differences between benign and malignant moles
A number of characteristics allow you to accurately determine which moles are dangerous:
A benign formation is not asymmetric. If you draw a line through the middle, then both sides will correspond to each other. Cancer seal does not meet these requirements.
Unlike, the usual pigmented spot has smooth, not jagged borders.
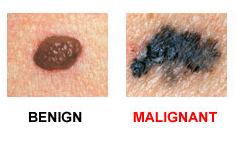
The presence of color and brightness is another exciting symptom.
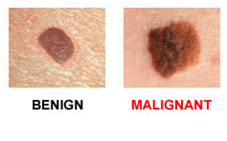
Education changes size over time and becomes larger than 6 mm. Noncancerous nevi look the same. You need to be on the lookout if or gives other unusual signals regarding her general condition.
The only way to accurately establish the diagnosis and confirm or refute is to conduct a histological examination of the cells using a biopsy.
Dangerous moles: symptoms of melanoma
Cancer pigmentation can vary greatly in its symptoms. Sometimes a person is able to adequately assess only some of the features. You should pay attention to how a dangerous mole looks like:
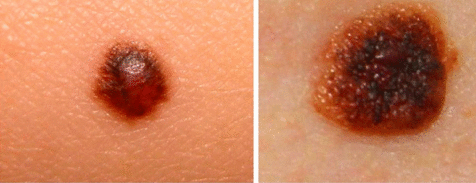
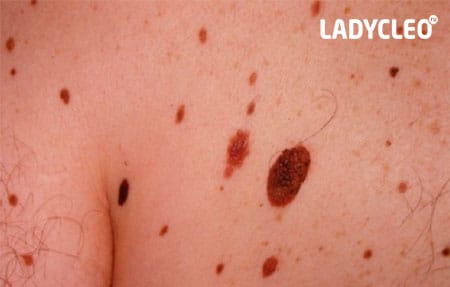
Irregular edges, but a fairly clear border with healthy tissue. Diameter - 10 mm.
A blue-black, newly formed melanoma that has irregular borders. It originated from a dysplastic nevus (pink-brown area in the upper left corner). The size is about 12 mm.
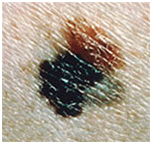
Oncological dysplastic nevus with a black distant malignant extension that was previously absent. It is only about 3 mm.
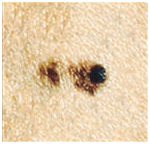
Malignant skin tumor consisting of three parts: dark brown delimitation on the left, red on the right, and a light area on top. The size is about 15 mm.
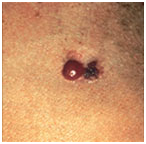
Photos of dangerous moles on the body
Melanoma in a dysplastic nevus: irregular contours, bright color, relatively small size (1/3 inch).
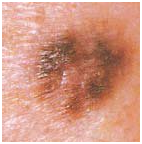
Transformation of solitary atypical pigmentation with black, brown and pink (1/2 inch).
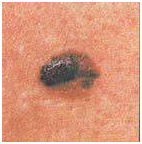
Oncoformation on the lower back demonstrates asymmetry, color saturation, and changes in the border zone with healthy skin.
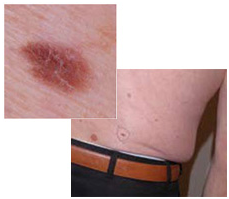
Each person should be attentive to the condition of their skin in order to diagnose and prevent possible consequences that are detrimental to health and life. Remember that if detected early, skin cancer can be successfully treated.
Malignant moles are identified by symmetry, diameter, texture, color, and other features. They are of several types: borderline blue, giant, Oto, Dubreuil's melanosis.
Moles oncology
In the photo, a type of mole - melanomaMoles (birthmarks) - pigmented formations on the skin, which are congenital or acquired, have a different color (black, purple, red, brown). Often they are called nevi. They also differ in convex or flat, with a hairy or smooth surface. Formations appear on any part of the body and come in various sizes.
By themselves, such growths do not cause danger to the human body, however, under the influence of certain negative factors, they can degenerate into malignant formations, which are called melanoma-dangerous.
Dangerous moles - signs
To identify cancerous moles and recognize them among benign formations, visual diagnostics is carried out according to the following characteristics:
- symmetry - non-hazardous formations are symmetrical, that is, when a line is visually drawn through them, both sides correspond to each other (if asymmetry is observed, it is recommended to urgently contact a specialist);
- clear boundaries - in a normal formation, the edges are even, the boundaries are clearly defined, in contrast to poor quality;
- color - many formations that do not lead to negative consequences have one shade, and dangerous ones have a different one;
- diameter - usually harm to health is represented by large or sharply increasing in volume moles;
- texture change and vagueness - if the formations are normal (not cancerous), they do not change texture and do not blur over time.
It is important to carefully observe the dark and colorless (white) formations on your body, pay attention to how they look. If they begin to change, this is an occasion to consult a doctor. It should also be remembered that not all oncological formations behave in the same way, which complicates the diagnosis.
Types of dangerous neoplasms with a description
There are five types of dangerous nevi:
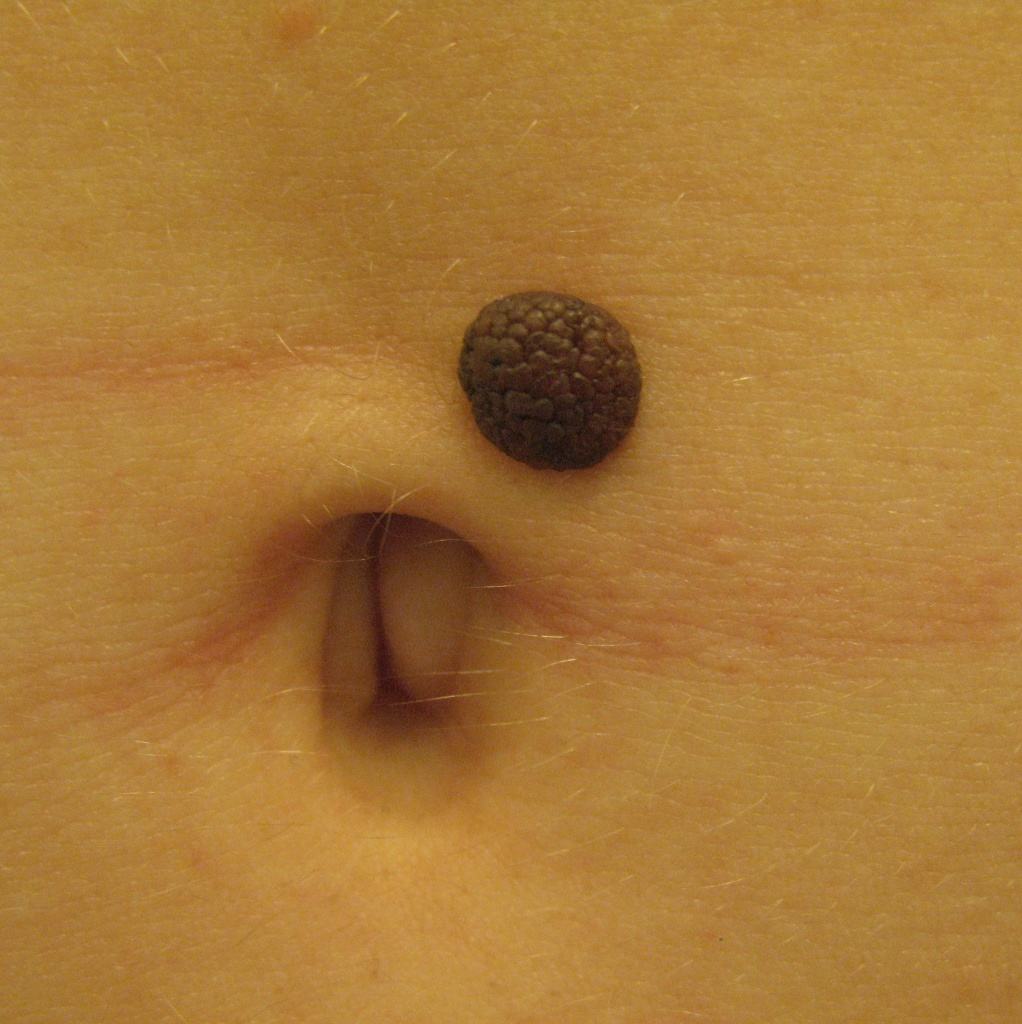
People at Risk
Certain factors contribute to the degeneration of ordinary formations into malignant ones. These include prolonged exposure to the sun, genetic predisposition, trauma.
The following groups of people are predisposed to the formation of malignant tumors on the skin:
- with a large number of moles (more than fifty) - it is advisable for such people to avoid the sun or limit the time spent under its rays, it is recommended to use an umbrella for this purpose, wear closed clothes, hats;
- with snow-white skin and bright red hair from nature;
- in old age - according to research results, older people are more likely to suffer from skin cancers than young people, besides, their treatment makes it difficult to have concomitant chronic diseases;
- during pregnancy;
- with a lot of freckles - people who have a lot of freckles on their body are most often prone to cancers on the skin.
For reasons unknown to science, melanoma is more common in men than in women.
Diagnostic methods
It is possible, but difficult, to determine a dangerous formation on the skin on your own. Therefore, it is important to contact a dermatologist who, after examination, will give a referral to another specialist if he considers it necessary (to an oncologist or surgeon).
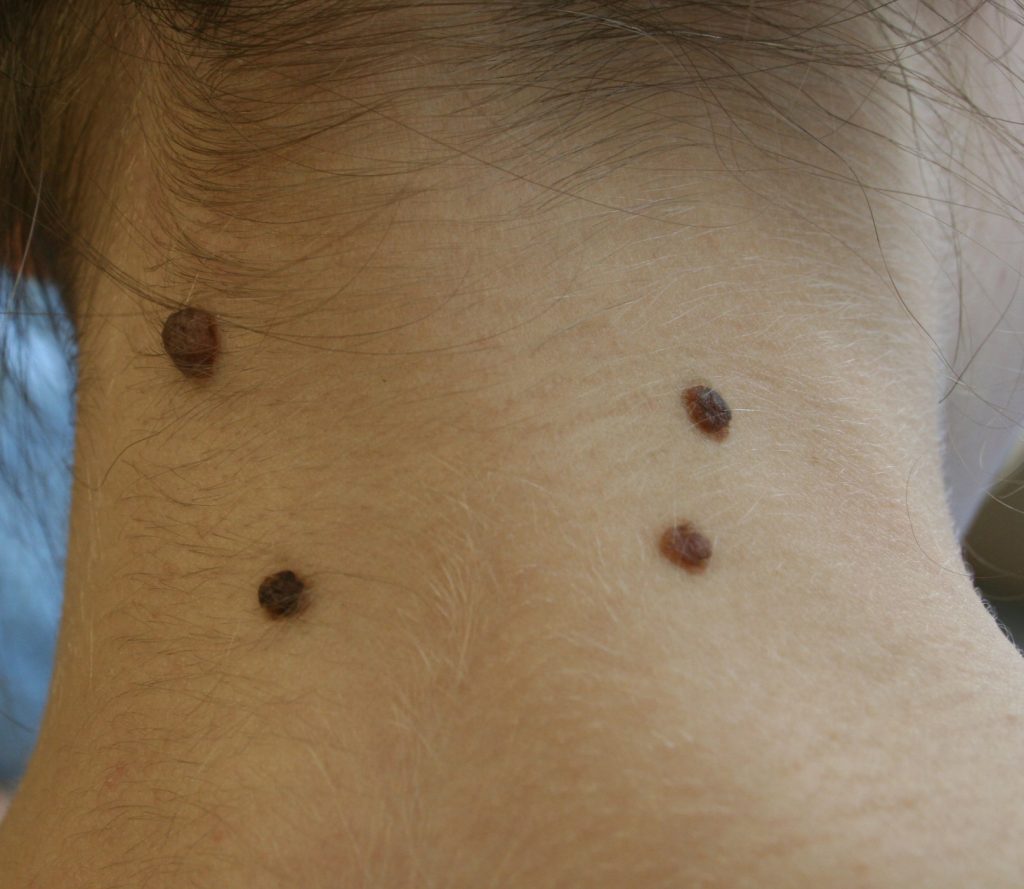 Photos of different types of moles
Photos of different types of moles Diagnostic examination of moles is called dermatoscopy. It doesn't hurt and doesn't take long. For the procedure, a special device called a dermatoscope is used. First, the doctor applies a gel to the patient's skin, which will eliminate possible visual interference (for example, light refraction). This is followed by a visual inspection. If necessary, macro photography and additional studies of the obtained images are performed. The diagnosis is established with an accuracy of 97%.
Removal of formations
Indications for the elimination of dangerous formations:
- cancer cells are detected;
- permanent injuries, resulting in deformation of the mole, it bleeds, hurts, causes discomfort;
- large size of the formation and unaesthetic appearance.
Unfortunately, many patients do not turn to specialists in time.
Known ways to get rid of moles:
- laser therapy;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave method;
- surgical method.
Laser therapy uses local anesthesia. The procedure is done with a laser. The advantage of this method is the simultaneous coagulation blood vessels. This means that laser therapy is particularly suitable for bleeding lesions.
Cryodestruction is the removal of formations using a mixture of low temperature liquid nitrogen or carbonic acid. The procedure is also performed under local anesthesia. The disadvantage of cryodestruction is the lack of precise control over the depth of exposure to nitrogen or acid, as well as the difficulty in collecting histological material for subsequent analysis. This procedure leaves scars on the skin.
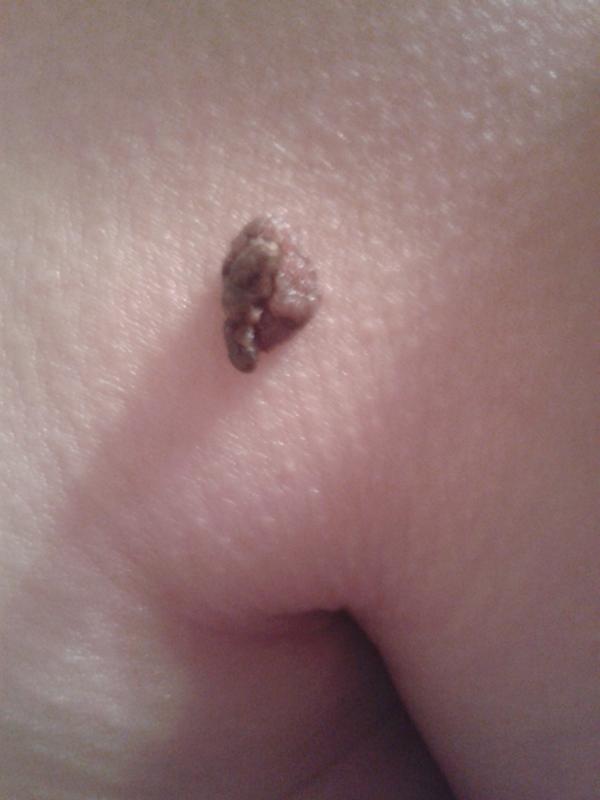 What dangerous moles look like in the photo
What dangerous moles look like in the photo During electrocoagulation, the neoplasm is burned out with an electric knife. Currently, this procedure is used quite rarely, since after it there is a high probability of scarring.
The radio wave method belongs to the hardware method for removing formations. Most often it is used to get rid of small moles. First, local anesthesia is performed, then the formation is irradiated on a radio wave apparatus. After this procedure, a wound remains.
In the case of a strong growth of melanoma or the presence of large formations, a surgical method is used. As a rule, a skin flap is also removed at the same time. Its depth and dimensions depend on the dimensions of the formation itself. The wound is sutured, the stitches are removed after a week. Local or general anesthesia is used for the operation.
To seize the moment and recognize dangerous symptoms when the growth on the skin begins to regenerate and pose harm to the body, it is important to conduct a thorough examination of your own body every two months. It is necessary to pay special attention to new formations that have arisen recently, as well as changes in old ones. To do this, it is advisable to use a magnifying glass, a ruler and other items that help to make measurements more accurately. It is impossible to remove any formations on your own, as this is fraught with negative consequences.
Almost everyone has moles. Someone has only a few of them, and some people can count dozens and even hundreds of such marks. Most moles are harmless formations. But among them there are spots that can cause a lot of trouble. What types of moles are distinguished and when do they require our close attention?
Morphological classification of moles
A mole in medical terminology is called a "nevus". This is an accumulation of cells - melanocytes, containing a special pigment - melanin. The color of the mole is due to the concentration, amount and depth of melanin in the nevus.
Moles are classified according to a number of parameters. They can vary in color, shape and size.
Color
The color scheme of the spots is varied. It depends not only on the characteristics of the cells that form the mole, but also on the color type of the human skin - the carrier. There is a palette:
- From light brown to almost black.
- Pink - red - crimson.
- Blue - purple - dirty blue.
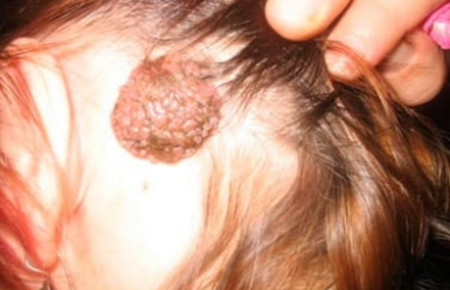
The form
Flat and convex, round and oblong, nodular and "pedunculated", smooth and rough - the dimorphism of the spots is impressive! As a rule, even on the body of one person, moles of various shapes can “get along” quite peacefully.
The size
From 1 mm to extensive nevi covering a significant area. As a rule, size is not directly related to the risk of nevus degeneration into an oncogenic form.
Attention! Any change in the shape, color, size and structure of the nevus is a sufficient reason to contact a dermato-oncologist for timely diagnosis!
Moles are considered safe if they have:
- smooth edges;
- no more than 0.5 cm in diameter;
- evenly colored.
Even the subjective feeling that a mole is different from the rest, and even more so - itchy, growing and changing color should alert. According to some reports, the 5-year survival after treatment of malignant tumors detected at an early stage reaches more than 90%.
![]()
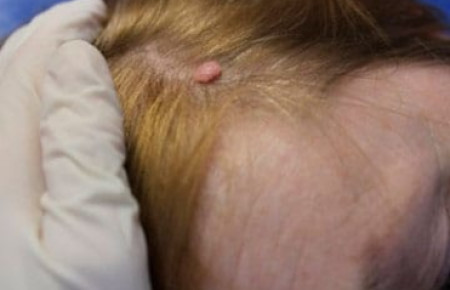
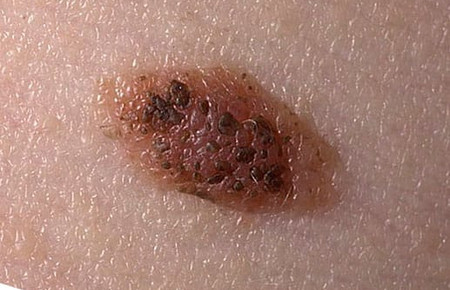
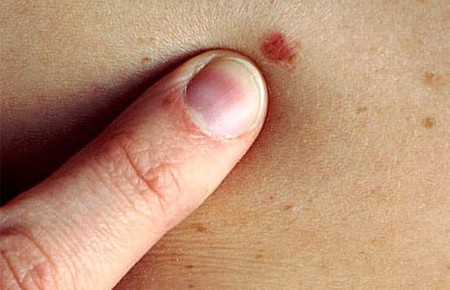
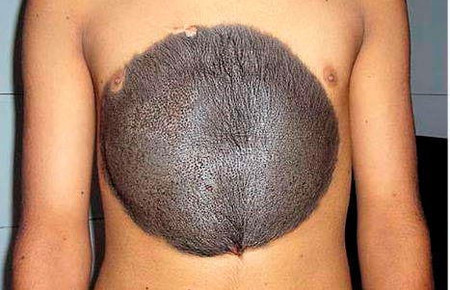
Types of moles on the basis of good quality
Morphological features of moles provide primary information about their structure and character. A complete picture can only be revealed by histological examination. So, there are three conditional groups of skin neoplasms:
- Benign neoplasms - nevi.
- Precancerous or borderline - basilioma.
- Malignant - melanoma, skin cancer.
Benign nevi
Widespread. We can say that upon close examination, they can be found in the majority. In such plaques, the edges are even and clear, they can be of various solid colors. Able to increase in size, but this process is slow and often goes unnoticed. Their growth is not associated with discomfort - it does not cause itching and inflammation.
Borderline neoplasms
These include potentially dangerous pigmented formations - atypical moles and basiliomas. When certain conditions are created (trauma, excess sun), they can turn into a malignant form. There is a simple formula - the abbreviation AKORD. With its help, you can try to independently determine the presence of an atypical mole.
A - asymmetry;
O - color;
P - size;
D - dynamics.
An atypical asymmetrical mole with jagged edges of uneven color, changing its size and changing its appearance.
Malignant structures
Melanoma, or skin cancer, is less common. According to some reports, only one mole out of a thousand is fraught with danger. However, in some countries, doctors began to remove all pigmented formations on the skin without waiting for their rebirth. In Russia, this method of combating melanoma is not practiced. And there is a good reason for this - the removal operation itself can also cause a malignant change.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to visually determine the degree of malignancy of a mole. And the line between them is so thin that in case of any suspicion it is better to consult a doctor. The presence of atypical spots suggests careful observation and inspection every three months.
Structural classification
According to the structures involved in the body of the mole, dermatologists distinguish between pigmented, vascular and warty varieties.
Pigmented moles
Appearance - smooth or rough, may have hairs coming from the inside. Color varies, but in all cases darker than freckles. The color of pigmented nevi is due to a combination of black eumelanin and brown pheomelanin.
The composition of pigmented nevi includes two types of cells - epidermal and sheaths of nerve cells located in the upper layers of the skin.
![]()
Vascular moles
Nevi of this type lie deeper, localized in the basal layer of cells between the epidermis and dermis. They are more convex and include blood vessels in their structure. The color of such formations is from pink to bright red.
warty moles
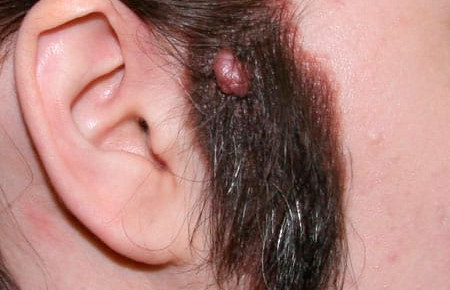
Accumulation of blisters that are dirty gray or brown in color. The surface is granular, keratinized. The external resemblance to a wart determined the name. Mostly localized on the head, neck, behind the ears.
More often, a warty nevus is found in the fair sex. Unfortunately, these moles do not add charm to them, since they are large in size, highly visible in the photo and have an unpleasant appearance. From 2 to 10% of such formations can degenerate into cancer, and therefore require careful attention and observation by a dermatologist.
medical classification
Nevi are diverse and changeable - the variety of their forms, structures and degree of danger requires different approaches to classification. Let us describe the types of moles that are distinguished by practicing dermatologists when making a diagnosis.
Lentigo
Somewhat reminiscent of freckles. The main difference is a more saturated color. In addition, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the number of such spots and the intensity of their color does not change. Border formations located in the basal layer between the epidermis and dermis.
epidermal-dermal
They are non-convex nevi of small size up to 1 cm. Like lentigo, they are based in the border area. Skin to black color. Localized on the skin of the feet, palms and in the genital area.
Intradermal nevi
The melanocytes that form this type of nevus are located in the thickness of the dermis. The deeper the melanocytes lie, the more convex the nevus. In this case, the plaques necessarily protrude above the skin. Color - from beige to dark brown.
Complex nevi
Melanocytes of such a nevus are located both in the dermis and in the epidermis. These moles always protrude above the skin and are very dark in color.
Nevi of Sutton
A characteristic feature of this type is the ability to spontaneously disappear and appear. They are easily distinguished from others by the presence of a ring of unpigmented skin around the nevus.
Dysplastic nevi
They have a number of characteristic features:
- They first appear in people over 35 years of age.
- Diameter - up to 12 mm.
- They are located in areas hidden from sunlight (buttocks, chest, scalp).
- Often these are numerous clusters.
- Passed down by inheritance.
- Paradoxically, these irregularly shaped plaques with a blurry edge and uneven coloring, although fraught with signs of cancer, rarely turn into malignant forms.
Blue nevi
The color scheme of such nevi is diverse - from gray-blue to blue and dark blue. hallmark- color variations within the blue palette. These are towering formations with a smooth surface and a clear border. The size does not exceed 2 cm, hair does not grow in their area. Located on the face, limbs and buttocks.
Cell blue nevus
Visually, this type of nevus is indistinguishable from a simple blue nevus. Histological examination shows that this type of mole is distinguished by the ability to rapidly divide melanocytes. This is an unfavorable sign indicating the possibility of developing melanoma.
Giant pigmented nevus
It is a flat spot, the color of which can be either brown or dark gray. It can reach an impressive size, since it is an innate formation that tends to grow with the child.
Nevi of early childhood
In addition to the giant pigmented nevus, there are other congenital pigmentation disorders. As a rule, these are vascular types of moles, namely hemangiomas, wine stains and pigmentation at the base of the skull. The latter passes on its own within 1 - 1.5 years.
Hemangioma
Benign formations that have developed during the malposition of a blood vessel. They appear within the first week of life and look like a pink-red spot the size of a needle point. For some time they may increase slightly in size, but in most cases they turn pale and disappear by 3 years.
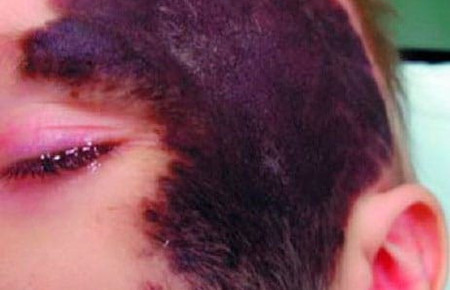
wine stains
Their other name is flaming nevi. Occur due to the expansion of blood vessels on the face and scalp. With age, they do not disappear and do not turn pale, but grow with the child. If such a spot appears, it is better to immediately contact a dermatologist and start treatment as early as possible in order to prevent it from growing and becoming a serious cosmetic defect.
Take care of yourself and your loved ones! Visit a dermatologist, study your moles - this will give you peace of mind and confidence in your health.
